AI Capability Terrain: Mapping the Frontier and Sinkholes of AI Progress
Published:
Overview
AI Capability Terrain is a system for visualizing and forecasting AI progress by combining three complementary perspectives — baseline capabilities, frontier forecasts, and systematic sinkholes. It uses logistic growth modeling to project when state-of-the-art AI systems will hit critical performance thresholds (85%, 90%, 95%) across 30+ benchmarked capabilities, achieving an average R² > 0.95 on historical data.
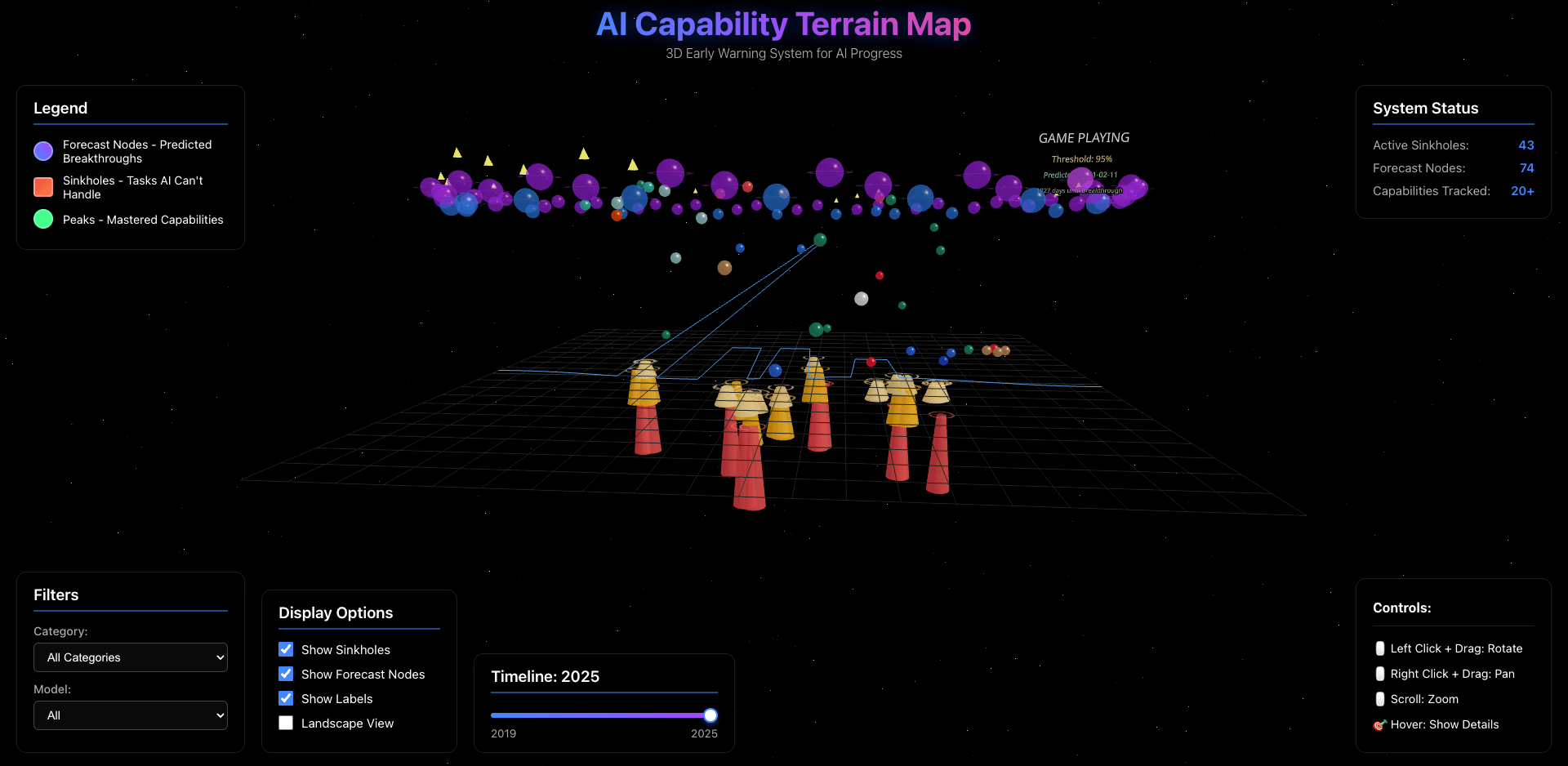
The system also identifies “capability sinkholes” — tasks that remain persistently difficult despite rapid progress in related domains — and visualizes them on an interactive 3D terrain map, giving a unified, interpretable view of the AI capability landscape.
Motivation
AI forecasting is often fragmented across timelines, benchmarks, and opinions. This project addresses that by building a reproducible, data-driven framework that quantifies and visualizes AI progress with uncertainty estimates. The work was conducted as part of the Apart Research Forecasting Sprint (2025) to improve how researchers and policymakers track capability trajectories and detect blind spots in AI development.
Technical Details
Technologies Used
- Python — data processing, modeling, and simulation
- JavaScript — interactive 3D visualization and UI controls
- Jupyter Notebook — analysis, experimentation, and reproducibility
- CSS & HTML — layout, styling, and web integration
Architecture / Approach
The pipeline consists of five main components:
Data Ingestion & Normalization:
Handles heterogeneous benchmark formats (0–1, 0–100, 1–10). A custom scale-detection algorithm standardizes data to a unified percentage scale.Logistic Growth Modeling:
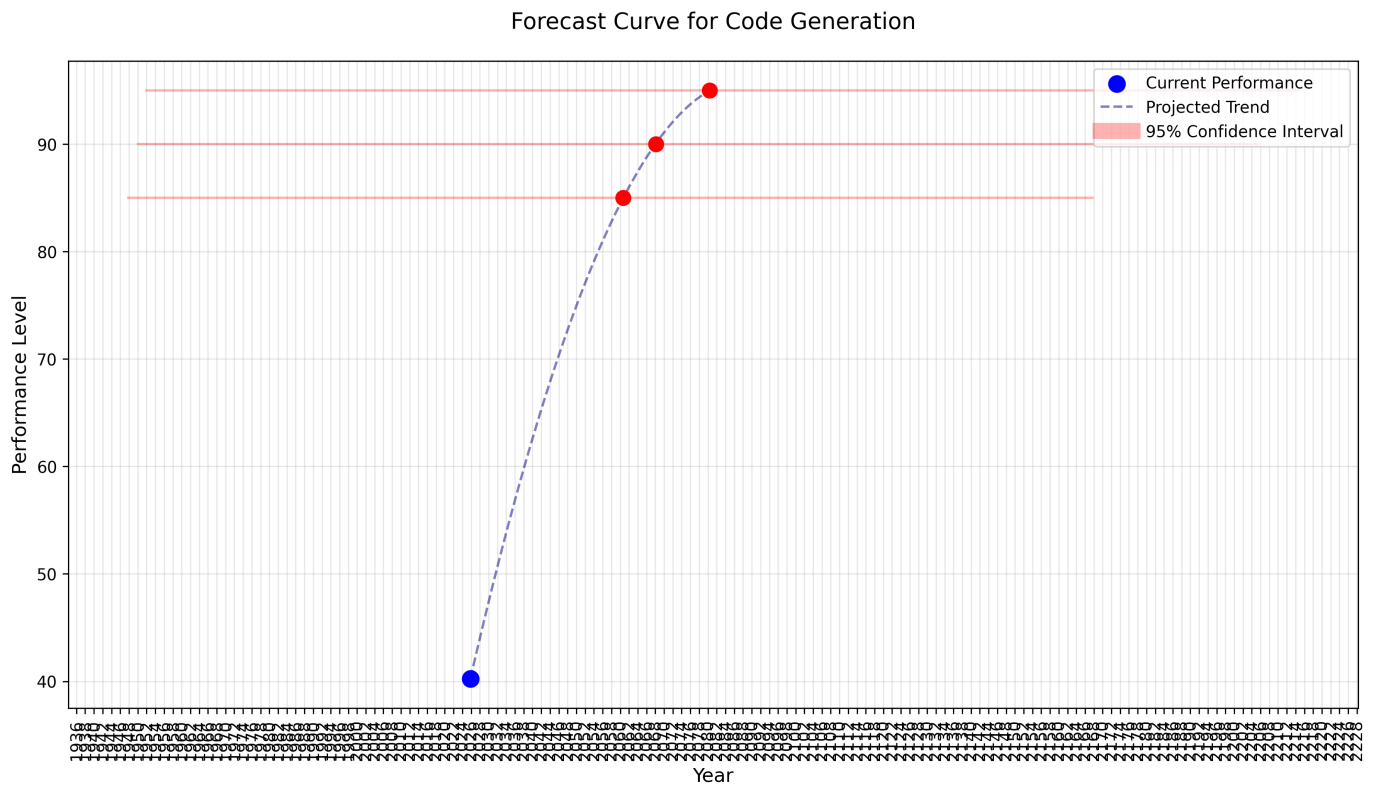
Each capability is independently fitted with a logistic growth curve using SciPy’scurve_fitand Levenberg–Marquardt optimization. The model captures realistic S-shaped progress curves.Uncertainty Quantification:
Confidence intervals (95%) are estimated through Monte Carlo simulation (10,000 samples), drawing from parameter covariance to derive threshold-crossing dates.Sinkhole Detection:
Identifies tasks that underperform relative to related capabilities (e.g., spatial reasoning, constrained generation). Severity is rated from low to critical depending on cross-model failure rates.Visualization Integration:
Forecast results are exported as JSON meshes for rendering in an interactive 3D terrain map, with consistent color and opacity schemes.
Key Features
- Automatic Scale Detection: Corrects mixed scoring formats across 40+ benchmarks
- Confidence Interval Forecasting: Logistic fits with R² > 0.95 across 24 valid capabilities
- Sinkhole Detection: Identifies and categorizes systemic blind spots
- Interactive Terrain Map: Visualizes baseline, forecast, and sinkhole layers in 3D
- Unified Export Schema: Ready-to-visualize JSON output for reproducibility
Results / Outcomes
- Achieved mean R² = 0.96, confirming logistic growth as a reliable forecasting model.
- Near-term forecasts: general knowledge (mid-2026), CAD design (late 2026).
- Long-term lagging capability: mathematical reasoning (~2028 ± 8 mo).
- Identified critical sinkholes in constrained generation, spatial reasoning, and self-reference tasks.
- Confidence interval analysis showed tight bounds (≤6 months) for mature capabilities and wide ones (>12 months) for immature domains.
What I Learned
- Handling heterogeneous benchmark formats is essential for valid forecasting.
- Confidence intervals communicate far more nuance than single-point predictions.
- Data visualization can bridge technical forecasting and policy discussions effectively.
- Persistent “sinkholes” may indicate deeper architectural limits, not just lack of data.
Future Work
- Add ensemble forecasting and anomaly detection for better robustness
- Model inter-capability dependencies
- Automate sinkhole detection using correlation networks
- Integrate updated benchmarks from Epoch AI and Metaculus
Status: Completed | Timeline: Nov 2025 Collaborators: Kalpesh Panchal (Ministry of Ontario), Apart Research
